As you step forward, your foot rolls slightly inward to distribute the impact of your stride. This natural movement is known as pronation and is essential for proper biomechanics during walking and running. But what exactly does pronation entail, and why is it so important?
Pronation refers to the way your foot moves to absorb shock and help maintain balance with each step. It involves a series of coordinated movements that ensure your body remains stable and efficient. Let’s explore the different types of pronation to understand their impact on your health and performance:
Types of Pronation
- Normal/Neutral Pronation: In normal pronation, your foot rolls inward about 15%, which is ideal for absorbing shock and providing balance. This natural inward roll helps distribute the impact evenly as you walk or run.
- Underpronation (Supination): Here, the foot rolls outward instead of inward. This is common in individuals with high arches and can lead to conditions like Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and IT band syndrome. Underpronation often results in insufficient shock absorption, increasing the risk of injury.
- Overpronation: This occurs when the foot rolls inward more than 15%, often associated with ‘flat feet.’ Overpronation can strain muscles and joints, leading to injuries such as IT band syndrome. It disrupts the natural alignment, increasing the likelihood of discomfort and injury over time.
Understanding these types of pronation can guide you in choosing the right footwear and potentially addressing any biomechanical issues. Whether you are walking or running, recognizing your pronation type is a step toward better performance and injury prevention.
What Is Excessive Pronation?
Excessive pronation, or overpronation, refers to the inward rolling motion of the foot that goes beyond the normal range during the gait cycle. In a healthy gait, the foot rolls inward slightly to absorb shock and adapt to different terrains. However, when overpronation occurs, the foot excessively flattens, causing the arches to collapse and the ankles to roll inward excessively.
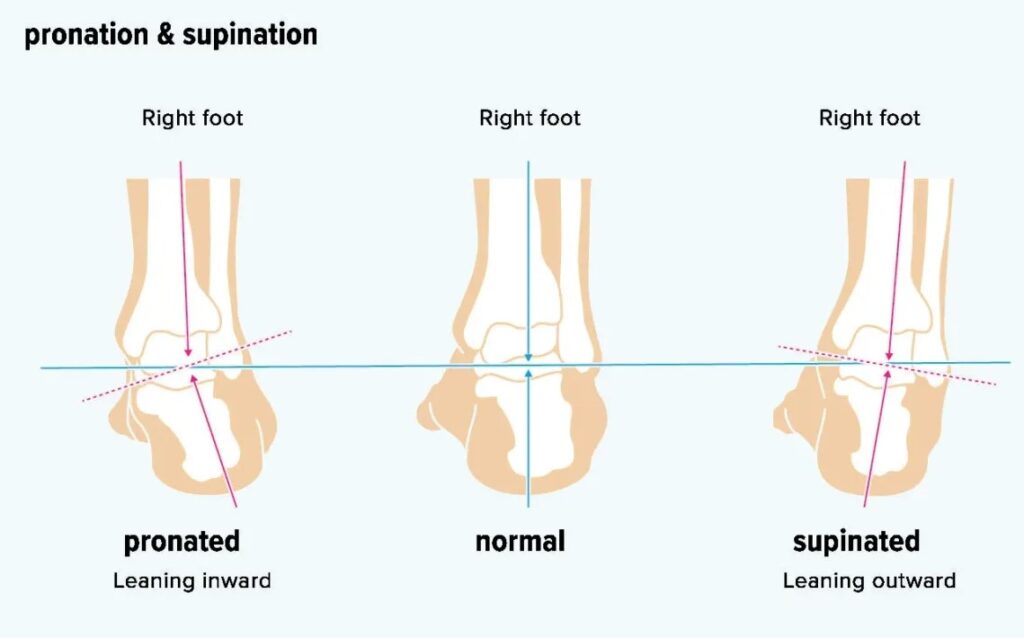
What Are the Types of Pronation?
Understanding the types of pronation can help you choose the right footwear and prevent common foot injuries. Pronation is essentially how your foot rolls when it makes contact with the ground. Here’s a breakdown of the three main types:
1. Neutral Pronation
Neutral pronation provides a comfortable balance, where your foot rolls inward slightly, about 15%. This natural movement helps absorb impact and keep you steady with each step. Most individuals with neutral pronation have an efficient gait that supports even distribution of body weight.
2. Underpronation (Supination)
Underpronation, or supination, occurs when the foot rolls outward upon impact. Those with high arches are more susceptible to this condition, which can lead to issues such as Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and iliotibial (IT) band syndrome. Supinators often experience less shock absorption, meaning their shoes should offer extra cushioning and flexibility.
3. Overpronation
Overpronation is identified when the foot rolls excessively inward, more than the typical 15%. Common among individuals with flat feet, this condition can also predispose them to injuries like IT band syndrome. Stability or motion-control shoes are often recommended to help manage overpronation and reduce the risk of injury.
Understanding your pronation type can guide you in selecting the appropriate footwear, potentially enhancing comfort and performance in your daily activities.
Causes of Excessive Pronation
Several factors contribute to the development of excessive pronation. Some of the primary causes include:
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in foot structure and mechanics. If you have a family history of overpronation, you might be more prone to experiencing excessive pronation yourself.
Flat Feet
Individuals with low arches or flat feet have a higher tendency to experience overpronation. Flat feet fail to provide adequate support to the body, leading to an increased risk of pronation-related issues.
Foot Injuries
Injuries to the foot or ankle, especially if not treated properly, can alter the foot’s biomechanics, leading to overpronation.
Improper Footwear
Wearing shoes with inadequate support or improper arch support can contribute to overpronation.
Lifestyle Factors
Engaging in certain activities and sports that require repetitive movements, like running or dancing, can elevate the risk of overpronation.
Identifying Excessive Pronation: Common Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of excessive pronation is crucial for timely intervention. Here are some common symptoms associated with overpronation:
Arch Pain
People with excessive pronation often experience pain or discomfort in the foot’s arch due to the increased strain on the plantar fascia.
Heel Pain
Overpronation can lead to plantar fasciitis, a condition characterized by inflammation and pain in the heel area.
Ankle Pain
The unnatural inward rolling motion can cause stress on the ankle joint, leading to pain and potential injuries.
Knee Pain
Excessive pronation may result in misalignment of the leg bones, leading to knee pain and discomfort.
Shin Splints
Shin splints are a common complaint among those with overpronation, as excessive strain on the shin muscles can lead to inflammation and pain.
How to Test for Overpronation with the Water Test
Are you wondering if you overpronate when you walk or run? A quick and simple method to find out is the water test. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform it, along with what to look for to identify overpronation:
Materials Needed
- A shallow dish of water
- A piece of cardboard or paper that can absorb water
Steps to Perform the Water Test
- Prepare Your Surface
Place a piece of cardboard or thick paper on a flat area. Make sure it’s large enough to capture your entire footprint. - Wet Your Foot
Dip one foot into the shallow dish of water, ensuring the sole is evenly wet but not soaking. - Make Your Footprint
Step onto the prepared surface with your wet foot. Ensure you transfer your weight naturally, as you would when walking, to get an accurate imprint. - Examine the Footprint
Carefully step off and observe the pattern left behind.
Analyzing the Results
- Overpronation Identification
- If the middle part of your footprint is wide, filling in most of the area: This indicates overpronation, where your foot rolls inward excessively.
- Neutral Foot Print
- A balanced footprint will display a moderate curve with a distinct midsection, indicating a neutral pronation.
- Supination Check
- A footprint with a narrow or nearly absent middle section suggests supination, where the outer edge of your foot bears more weight.
By using the water test, you can quickly gain insights into your foot’s pronation tendencies. This can help inform your choices for running shoes or orthotics tailored to your specific needs.
How to Perform a Wear Test to Check for Overpronation
Wondering if you overpronate when you run or walk? A simple wear test can help you find out by analyzing the wear patterns on your running shoes.
Step-by-Step Wear Test
- Examine Your Shoes: Grab a pair of well-worn running shoes. It’s important they have enough mileage to show distinct wear patterns.
- Inspect the Inner Sole: Look at the inner edge of the shoe, from the area around the big toe to the ball of the foot. Overpronation often results in excessive wear along this path.
- Compare Different Sections: Observe how the wear compares from the inside edge to the center and outer edges. For neutral pronation, wear is usually centered around the toes and heel, while overpronation will emphasize the inner edge.
- Spot Outer Edge Wear: If you notice more wear on the outer side (pinky toe down to the heel), you’re likely looking at supination, not overpronation.
- Assess Beyond the Soles: Sometimes, the shoe’s upper might show signs of stretching, particularly on the inner side, which also indicates overpronation.
Why Conduct a Wear Test?
Understanding your foot’s pronation can improve your comfort, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance performance. Once you know your pattern, you can select footwear specifically designed to combat overpronation, making your runs more enjoyable and efficient.
The Impact of Excessive Pronation on the Body
Overpronation can have a cascading effect on the body. It affects the feet and ankles and can lead to problems in other body areas, such as the knees, hips, and lower back. The misalignment caused by overpronation can alter the body’s posture and gait, leading to chronic pain and discomfort if left untreated.
Excessive pronation begins with the foot’s natural movement. As you walk or run, your foot is designed to roll slightly inward to absorb shock. However, when the arches of the foot—especially low or flexible ones—collapse inward more than normal, overpronation occurs. This excessive inward rolling results in the foot becoming an unstable platform, straining the toes and causing the lower leg to rotate excessively.
Recognizing Overpronation in Your Running Shoes
When examining your running shoes, identifying signs of overpronation can help optimize your running experience. Overpronation occurs when your foot rolls inward excessively during each step, potentially leading to discomfort or injury. Here’s how to spot the signs in your footwear.
Shoe Wear Patterns
- Inner Edge Wear: Check the soles of your running shoes. Overpronation typically results in excessive wear along the inner edge, tracing a path from the big toe to the ball of the foot. This indicates that your feet are rolling inward more than they should.
- Insole Compression: Take a look inside your shoes. Over time, the insole may compress on the inner side, leaving a clear impression where the arch and big toe apply pressure. This characteristic pattern further suggests overpronation.
The Water Footprint Test
Another method to identify overpronation is the water test, which gives insight into your foot’s arch behavior:
- Wide Footprint: Wet your foot and step onto a dry surface like cardboard. If you see a wide print through the middle, your foot may be overpronating, as more of it comes into contact with the ground.
Being aware of these signs enables you to make more informed choices when picking running shoes designed to address overpronation, potentially enhancing both comfort and performance. Brands such as ASICS, Brooks, and New Balance offer specialized options aimed at correcting this issue, helping you maintain a balanced stride.
The Mechanics of Overpronation
- Foot Flexibility: When the foot remains too flexible throughout the gait cycle, it acts as a mobile adaptor, failing to provide the needed stability.
- Arch Collapse: Low arches allow the foot to sink inward, further destabilizing the gait.
This instability doesn’t just affect the feet. It can cascade upward, influencing the alignment of the entire body. The strain on the tendons and ligaments, particularly those attached to the heel, can lead to heel pain and additional tension. This misalignment can cause discomfort not only in the feet and ankles but also travel upwards to affect the knees, hips, and lower back over time, manifesting as chronic pain if not properly addressed.
Effective Treatment Options for Excessive Pronation
Fortunately, several treatment options can help alleviate the effects of excessive pronation and prevent further complications:
- Supportive Footwear: Investing in supportive shoes with proper arch support can help stabilize the foot and reduce overpronation.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom-made orthotic inserts can provide additional support and correct abnormal foot mechanics.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the foot and ankle muscles, promoting better alignment and reducing overpronation.
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Regular stretching routines and strengthening exercises can enhance foot flexibility and alleviate the overpronation effects.
- Rest and Ice: Resting the feet and applying ice to inflamed areas can relieve the pain and inflammation associated with overpronation.
Understanding the Role of Motion Control Shoes in Managing Overpronation
Motion control shoes are specifically designed to address and manage overpronation, a condition where your foot rolls excessively inward as you walk or run. This inward roll can lead to various discomforts and injuries if not managed properly.
Key Benefits of Motion Control Shoes
- Foot Alignment: These shoes help correctly align your foot by offering a sturdy framework that prevents excessive inward rolling. This promotes a healthy balance between pronation and its opposite, supination.
- Enhanced Support: Built with maximum support, motion control shoes feature a firm midsole and a well-structured design. This support stabilizes the foot, providing a consistent foundation for each step.
- Cushioning: Motion control shoes come with structured cushioning that absorbs impact and provides comfort. It’s particularly beneficial for those whose feet require additional stability during high-impact activities.
Choosing the right pair is crucial. Look for shoes labeled specifically for motion control or stability from reputable athletic brands. They ensure the support needed to minimize the risk of injury, enhancing both performance and comfort for overpronators.
Why You Should Avoid Going Barefoot if You Overpronate
If you overpronate, it’s crucial to reconsider the idea of going barefoot, even when you’re indoors. Here’s why:
1. Minimizing Injury Risk:
When you overpronate, your feet roll inward excessively, which can lead to distributing weight unevenly. This instability increases the risk of injury, much like wearing shoes that can easily bend in half. Shoes with adequate support help maintain proper alignment, reducing potential harm.
2. Supporting Your Feet and Legs:
Going barefoot means your feet lack essential support, causing undue strain, especially when overpronation is a factor. Wearing supportive shoes or slippers indoors can alleviate this stress, offering the necessary cushioning and stability to protect your feet and legs from fatigue and pain.
3. Enhancing Comfort:
The absence of footwear might seem comfortable initially, but over time, it can lead to discomfort due to prolonged stress on your arches and heels. Supportive shoes or slippers are designed to combat these effects, ensuring comfort throughout the day.
In summary, investing in supportive footwear is a smart choice for those who overpronate, helping to prevent injuries and enhance daily comfort.
Understanding Motion Control Shoes
Motion control shoes are designed for those who need extra support to maintain proper foot positioning. These shoes are particularly beneficial for individuals who overpronate, helping them walk or run with a balanced alignment.
Key Features of Motion Control Shoes:
- Maximum Support: These shoes provide exceptional support, making sure your foot stays in the correct position throughout your activity. This minimizes the risk of injuries related to improper foot movement.
- Structured Cushioning: Their cushioning is tailored to provide firmness where it is needed most. This helps to stabilize the foot, offering a secure environment for the heel and arch.
- Rigid Soles: To assess the rigidity, try bending the shoe. A motion control shoe will not easily bend in half, indicating its robust structure that supports your foot throughout its stride.
- Pronation Control: They actively work to counteract excessive pronation by encouraging a natural gait and reducing stress on the feet and legs.
- Enhanced Durability: The materials and construction of these shoes ensure longer wear, particularly beneficial for those who regularly walk or run.
In summary, motion control shoes merge stability and durability with advanced features that support foot alignment, making them a critical choice for anyone needing extra foot support.
Preventing Excessive Pronation
Prevention is always better than cure. To minimize the risk of excessive pronation, consider the following preventative measures:
Choose the Right Footwear
Opt for shoes with good arch support and proper cushioning to support your feet adequately.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying excess weight can place additional pressure on your feet, worsening the effects of overpronation.
Warm-Up Before Physical Activity
Performing warm-up exercises before engaging in physical activities can prepare your feet and reduce the risk of injuries.
Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to any discomfort or pain in your feet and seek professional advice if needed.
Example of Pronation:
Imagine James, a dedicated basketball player in Orem who loves competing in local leagues. During a crucial game, he experiences a sharp ache in his foot and lower leg. Upon closer observation, he realizes that his foot tends to roll inward excessively every time he lands after a jump, causing his arch to collapse. His circumstance is an example of pronation, where his foot leans inward excessively. The discomfort hinders his performance, and he finds making quick and precise movements on the court challenging.
Wanting to address the issue, James seeks advice from a podiatrist. The podiatrist diagnoses him with overpronation and recommends combining exercises and custom orthotics to stabilize his foot and improve his alignment. Following the prescribed plan, James experiences a significant reduction in pain and gains better control over his movements on the court, ultimately enhancing his basketball performance.
What is Supination?
Supination is the opposite of pronation. It occurs when the foot rolls outward excessively during the gait cycle. While some supination is necessary for shock absorption, excessive supination can cause problems.
Impact of Excessive Supination:
Excessive supination can result in the following foot-related issues:
Ankle Sprains
The outward rolling motion of the foot can strain the ligaments on the lateral side of the ankle, increasing the risk of sprains.
High Arches
Excessive supination can cause the arches of the feet to become overly elevated, leading to high arches, which may result in reduced shock absorption and increased pressure on specific areas of the foot.
Stress Fractures
Excessive pressure on specific foot areas can increase the likelihood of stress fractures, particularly in the foot or lower leg bones.
Example of Supination:
Meet Sarah, an avid runner who hits the trails all throughout Utah County every weekend. During one of her trail runs, she suddenly feels a sharp pain on the outer edge of her foot and ankle. She stops and notices that her foot tends to roll outward with each step, putting excessive pressure on the lateral side of her foot. This is an example of supination, where her foot leans outward to an extreme degree. The pain intensifies as she continues her run, making it difficult to maintain her usual pace.
Concerned about her recurring discomfort, Sarah decided to consult a sports podiatrist. The foot doctor diagnoses her with excessive supination and recommends a pair of running shoes with additional cushioning and lateral support to correct her foot alignment. With proper footwear, Sarah gradually overcomes the pain and enjoys her favorite activities with renewed comfort and confidence.
Conclusion
Excessive pronation can significantly affect foot health and overall well-being. Recognizing its causes and symptoms can pave the way for early detection and prevention. While factors like genetics, weight, and lifestyle can contribute to excessive pronation, identifying its signs like flat feet or uneven shoe wear can prompt timely interventions.
Various treatment options, from suitable footwear and orthotics to physical therapy or surgery, can help mitigate the impact of overpronation. However, individual needs differ, making personalized advice from a podiatrist or healthcare professional vital, particularly in chronic or severe pain cases.
Always remember, your feet bear the weight of your body and your active life; they deserve the utmost care. With awareness, preventive measures, prompt treatment, and professional guidance, you can manage excessive pronation effectively and enjoy a healthy, active lifestyle.
Questions? Click Here to contact our office. We’re here to help.
